Issue:
When wind velocities are high it can cause soil erosion, snow drifting, airborne odors and pesticide drift. This can cause detrimental impacts on livestock, crop yields, pollinators, and enjoyment of your outdoor living spaces.
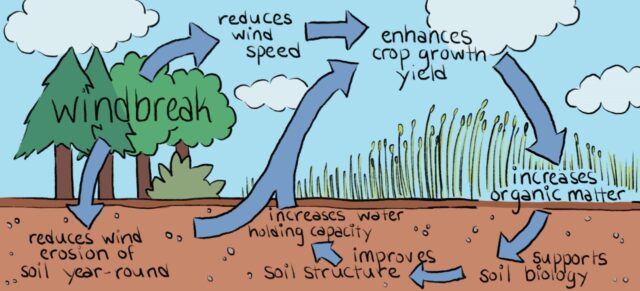
Functions & Benefits:
Windbreaks are living barriers oriented perpendicular to prevailing winds consisting of trees and shrubs designed to reduce wind speed. Established windbreaks protect livestock, increase crop yields, reduce wind erosion, reduce pesticide drift, filter dust and air pollutants, reduce noise. They can also reduce home heating costs by 10-25 percent! The extent of the sheltered area inside the windbreak depends on the height of the barrier, with the greatest wind reduction occurring between two to five times the height of the windbreak downwind.
How to Build Your Own:
- Evaluate the site conditions and identify areas that require wind protection.
- Determine the structure of the windbreak. Height, distance to the protected area, density, number of rows, length, orientation, and continuity will determine the effectiveness of the windbreak.
- Select species for the windbreak depending on your soil type and that provide beneficial habitat for wildlife. Evergreens should provide the “backbone” of the windbreak as they retain their leaves during the winter months.
- Plant your species in early spring while plants are still dormant for best success.
